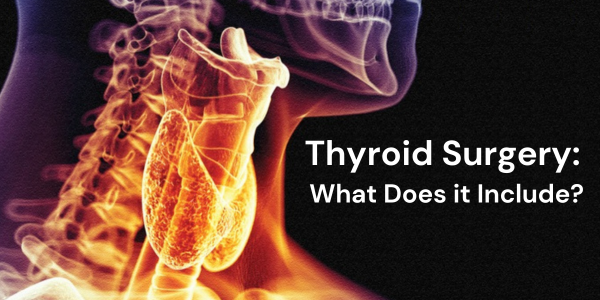
Thyroid surgery, or thyroidectomy, is a surgical procedure performed to remove all or parts of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It is crucial in regulating metabolism and producing hormones that control various bodily functions.
Thyroid Surgery Considerations: Knowing When It’s Appropriate
Thyroid surgery may be recommended for a variety of reasons, including:
- Thyroid Cancer: When cancerous cells are detected in the thyroid gland, surgery may be necessary to remove the cancerous tissue. Depending on the extent of the cancer, either a portion of the thyroid gland (partial thyroidectomy) or the entire gland (total thyroidectomy) may need to be removed.
- Benign Thyroid Nodules: Thyroid nodules are lumps or growths that form within the thyroid gland. While most nodules are non-cancerous (benign), they may still cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, breathing, or speaking, or they may be aesthetically undesirable. In such cases, surgical removal of the nodule (partial thyroidectomy) or a portion of the thyroid gland may be recommended to alleviate symptoms or prevent complications.
- Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to excessive production of thyroid hormones. In cases where medication or other treatments fail to adequately control the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, surgical removal of a portion of the thyroid gland (subtotal thyroidectomy) may be considered to reduce hormone levels.
- Goiter: A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, often caused by iodine deficiency, thyroid inflammation (thyroiditis), or other underlying thyroid disorders. If the goiter becomes large enough to cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or breathing, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary to alleviate pressure on surrounding structures.
Thyroid surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the specific approach depends on the reason for surgery and the extent of tissue removal required. It may be performed through a traditional open incision in the neck (open thyroidectomy) or using minimally invasive techniques such as endoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery. The choice of surgical approach is determined by factors such as the size and location of the thyroid gland, the presence of nodules or tumors, and the surgeon’s expertise.
Overall, thyroid surgery is a safe and effective treatment option for various thyroid conditions, and it can help improve symptoms, prevent complications, and in cases of cancer, provide the best chance of cure.
Types of Thyroid Surgery
Thyroid surgery, also known as thyroidectomy, involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. The type of surgery performed depends on various factors such as the nature and extent of the thyroid disorder, the presence of nodules or tumors, and the patient’s overall health. Here’s a detailed look at the different types of thyroid surgery:
- Total Thyroidectomy
A total thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure in which the entire thyroid gland is removed. This includes both the right and left lobes of the thyroid gland, as well as the isthmus that connects them. The purpose of a total thyroidectomy is to treat conditions affecting the entire thyroid gland, such as thyroid cancer, Graves’ disease (hyperthyroidism), large goiters causing compression symptoms, or multinodular goiters that cannot be managed conservatively.
Conditions that may require a total thyroidectomy:
- Thyroid Cancer: Total thyroidectomy is often recommended for thyroid cancer to ensure complete removal of cancerous tissue and to prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
- Graves’ Disease: In cases of severe or unresponsive Graves’ disease, total thyroidectomy may be performed to control hyperthyroidism and prevent complications.
- Large Goiters: Total thyroidectomy may be necessary for the treatment of large goiters that cause difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking due to compression of nearby structures.
- Multinodular Goiters: When multiple nodules develop within the thyroid gland and cause symptoms or concerns about malignancy, a total thyroidectomy may be recommended to address these issues comprehensively.
- Partial Thyroidectomy (Hemithyroidectomy)
A partial thyroidectomy, also known as a hemithyroidectomy, involves removing only one lobe (either the right or left) of the thyroid gland, along with a portion of the isthmus. This procedure is performed when the thyroid disorder is confined to one lobe or when preservation of thyroid function is desired. It is typically indicated for treating benign thyroid nodules, adenomas, or small thyroid cancers confined to one lobe.
Conditions Treated with Partial Thyroidectomy:
- Benign Thyroid Nodules: Hemithyroidectomy may be recommended to remove benign nodules causing symptoms or cosmetic concerns.
- Thyroid Adenomas: When a single adenoma (benign tumor) is present in one lobe of the thyroid gland, a hemithyroidectomy may be performed to remove the affected lobe while preserving thyroid function.
- Unilateral Thyroid Cancer: In cases where thyroid cancer is confined to one lobe of the thyroid gland and is small in size, a partial thyroidectomy may be considered as an alternative to total thyroidectomy, especially if the patient wishes to preserve some thyroid function.
- Thyroid Lobectomy
A thyroid lobectomy involves removing one lobe (either the right or left) of the thyroid gland, along with a portion of the isthmus. Unlike a hemithyroidectomy, which removes the entire lobe, a thyroid lobectomy preserves the contralateral lobe and most thyroid functions. This procedure is indicated when the thyroid disorder is localized to one lobe and there is no contralateral lobe or isthmus involvement.
Indications for a Thyroid Lobectomy:
- Unilateral Thyroid Nodules: Thyroid lobectomy may be performed to remove a solitary thyroid nodule or adenoma confined to one lobe of the thyroid gland.
- Suspicious Thyroid Nodules: If a thyroid nodule is suspicious for malignancy based on imaging studies or biopsy results, a lobectomy may be performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Follicular Neoplasms: Thyroid lobectomy may be recommended for the removal of follicular neoplasms, which have a lower risk of malignancy compared to papillary thyroid carcinomas but still require surgical intervention for definitive diagnosis and treatment.